Cybersecurity: 3 types of cyberattacks your company is exposed to
27/05/2021
8min
Tables des matières
Cyberattacks are no longer epiphenomena: 4 out of 5 companies say they have already been victims of cyberattacks.
One might also think that cybersecurity issues only affect very large companies. That's not true: in 2019, the average size of organizations victimized by ransomware was 645 employees. Regardless of the size of your organization, cybersecurity is a topic to be taken very seriously as crime is increasing and the consequences of attacks can be catastrophic.
"The banking sector is the most exposed sector to cyberattacks: +238% attacks worldwide since the start of the pandemic between February and April 2020."Source: VMware Carbon Black research firm
There are many types of cyberattacks in companies. Some are well known, others are more confidential and therefore more devious. Here are the main ones in this article.
Malware: public enemy number one
Malware is by far the most common cyberattack within organizations. In 2020, the cybersecurity company AV Test GmbH has counted more than one billion malware attacks worldwide:
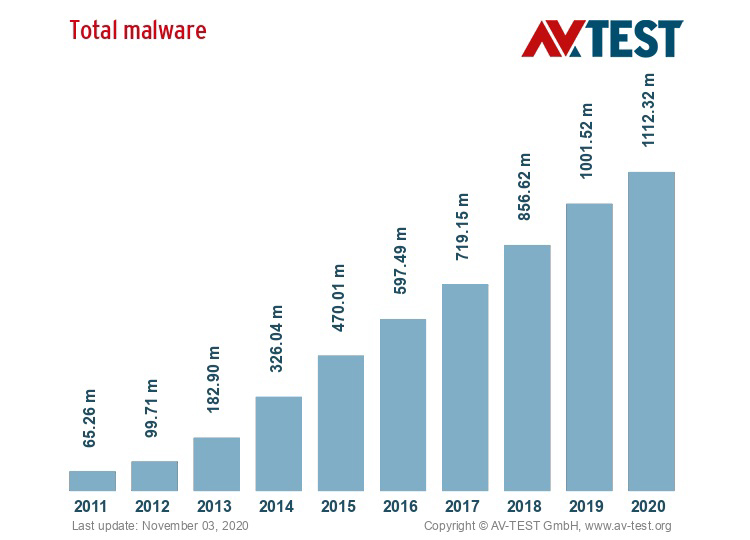
The most common types of malware in companies
The Trojan Horse
The term evokes cunning, the hidden introduction of the enemy. A Trojan Horse is a software program that copies the interface and operation of another program. Once triggered by the victim, the Trojan horse installs a parasite on his computer without the user noticing, at least in the first moments.
The Trojan horse serves as a "carrier" for the parasite to reach the targeted system, and will trigger its attack when it is installed on the target's terminal.
The botnet
A contraction of the term "robot" and "network", the botnet is a variant of the Trojan horse. Unlike the Trojan horse, the botnet does not act alone, but in a network. It is able to take control of several users/computers simultaneously while grouping them into a network of "bots" that can be managed remotely by cybercriminals.
Once deployed, the botnet can therefore act on a large scale and launch large-scale operations, such as DDoS attacks or spam campaigns.
The browser malware
Browser malware can be integrated directly into the search engine of a terminal. Once this malware is installed, it can modify your browsing and search settings. This type of malware has already been identified on most consumer browsers: Chrome, Firefox, Opera, Internet Explorer.
The ransomware
Ransomware is a real scourge as it has become more and more popular in the last few years. Ransomware is what is commonly called extortion software. Once it infects the "target" terminal, the ransomware can lock the computer and demand a ransom in exchange for a potential unlocking.
The point of sale malware
Point-of-sale (POS) malware is designed to steal payment data from its targets at the exact moment of the payment process on e-commerce sites.
Spyware
The sole purpose of spyware is to monitor and record all activities of the host terminal. It is not harmful in itself as it is not intended to degrade the functioning of a terminal, but it strongly compromises the privacy of organizations. Thus, the spyware can track visited websites, downloaded files, geographical location, contacts of an e-mailing service, e-mails, payment information, etc.
An example of malware in the insurance industry:

In May 2021, the company AXA Partnersa subsidiary of the French insurance giant, has been hit by a ransomware which damaged IT operations. Indeed, the ransomware managed to intercept some sensitive data that can be medical or financial. And there is no lack of examples. Insurance organizations are particularly exposed, as they handle a lot of sensitive personal data.
The previous summer, it was MMA that had to hastily bring its employees back on site while they were telecommuting, in order to counter a ransomware that had affected the insurer's business applications.
Don't forget! An effective cybersecurity organization is one with a CISO.
Phishing
Phishing is a cyberattack that consists in recovering the personal information of an Internet user or an organization. Phishing is particularly used to intercept victims' bank details. This method can be damaging for an individual as well as for a company employee.
Phishing is most of the time materialized by a fraudulent e-mail that impersonates an existing entity. It should be noted that companies in the banking and insurance sector are particularly affected by these cyber attacks.
The main types of phishing
Traditional phishing
Traditional phishing consists of impersonating a person to obtain confidential information and personal data. This widespread method is generally formalized by the usurpation of an individual's identity via his e-mail address. A traditional phishing campaign is often massive and untargeted.
Spear phishing
Spear phishing, unlike traditional phishing, targets a specific user or several employees of the same company. Here, cybercriminals gather as much information as possible about their victims and the people they are impersonating in order to make their target(s) fall into the trap.
Spear phishing allows the implementation of an equally popular method called the president scam (or BEC for Business Email Compromise). This is when a cybercriminal pretends to be the president of a company or group in order to build trust with the employees of the organization. The end goal is often to convince them to make an unscheduled international transfer to the cybercriminal organization.
The SMiShing
SMiShing, or SMS phishing, is the equivalent of traditional SMS phishing. These frauds are very common and much easier to set up because the layout requirements and customization possibilities are less, which makes it easier to spoof.
Misleading referencing
The DDos Attack
The DDos attack, or denial of serviceA DDoS attack is an attack whose sole purpose is to disable the operation of a service, a network, or a Web site. The DDoS attack consists of flooding the target server with connection requests or incoming messages in order to create a denial of service. To do this, cybercriminals hijack a very large number of computer systems and launch a targeted and grouped attack at a given moment. According to the latest WISR study, in 2019 there will be more than 8.4 million DDoS attacks.
Cybersecurity also means monitoring the vulnerability of applications. Are you interested? We also explain how to secure your application data.
The main DDoS attack vectors
Botnets
As seen above, DDoS attacks can be launched via botnets (networks of machines), in order to benefit from the simultaneous effect.
Reflection attacks
Amplification attacks
The amplification attack is a volumetric attack whose goal is to flood the bandwidth of the target network. This type of attack is made possible by modifying certain protocols to maximize the traffic generated on the network. This attack also has the particularity of generating a very large number of packets per second, which saturates the processing capacity of the target.
Cybercrime takes many forms, and attacks are becoming more and more frequent, regardless of sector or company size. It is therefore essential to call on specialists in the field of cybersecurity to define an effective defense strategy and set up reliable, watertight systems. For all these reasons, cybersecurity needs to be at the heart of a global strategy (see our article dedicated to the need to put cybersecurity at the heart of your Risk Management). It is therefore essential to implement Risk Management and internal control within the company.
From simple diagnostics to the most complex security projects, let our experts support you.
Cybersecurity: 3 types of cyberattacks your company is exposed to
27/05/2021
8min
Tables des matières
Cyberattacks are no longer epiphenomena: 4 out of 5 companies say they have already been victims of cyberattacks.
One might also think that cybersecurity issues only affect very large companies. That's not true: in 2019, the average size of organizations victimized by ransomware was 645 employees. Regardless of the size of your organization, cybersecurity is a topic to be taken very seriously as crime is increasing and the consequences of attacks can be catastrophic.
"The banking sector is the most exposed sector to cyberattacks: +238% attacks worldwide since the start of the pandemic between February and April 2020."Source: VMware Carbon Black research firm
There are many types of cyberattacks in companies. Some are well known, others are more confidential and therefore more devious. Here are the main ones in this article.
Malware: public enemy number one
Malware is by far the most common cyberattack within organizations. In 2020, the cybersecurity company AV Test GmbH has counted more than one billion malware attacks worldwide:

The most common types of malware in companies
The Trojan Horse
The term evokes cunning, the hidden introduction of the enemy. A Trojan Horse is a software program that copies the interface and operation of another program. Once triggered by the victim, the Trojan horse installs a parasite on his computer without the user noticing, at least in the first moments.
The Trojan horse serves as a "carrier" for the parasite to reach the targeted system, and will trigger its attack when it is installed on the target's terminal.
The botnet
A contraction of the term "robot" and "network", the botnet is a variant of the Trojan horse. Unlike the Trojan horse, the botnet does not act alone, but in a network. It is able to take control of several users/computers simultaneously while grouping them into a network of "bots" that can be managed remotely by cybercriminals.
Once deployed, the botnet can therefore act on a large scale and launch large-scale operations, such as DDoS attacks or spam campaigns.
The browser malware
Browser malware can be integrated directly into the search engine of a terminal. Once this malware is installed, it can modify your browsing and search settings. This type of malware has already been identified on most consumer browsers: Chrome, Firefox, Opera, Internet Explorer.
The ransomware
Ransomware is a real scourge as it has become more and more popular in the last few years. Ransomware is what is commonly called extortion software. Once it infects the "target" terminal, the ransomware can lock the computer and demand a ransom in exchange for a potential unlocking.
The point of sale malware
Point-of-sale (POS) malware is designed to steal payment data from its targets at the exact moment of the payment process on e-commerce sites.
Spyware
The sole purpose of spyware is to monitor and record all activities of the host terminal. It is not harmful in itself as it is not intended to degrade the functioning of a terminal, but it strongly compromises the privacy of organizations. Thus, the spyware can track visited websites, downloaded files, geographical location, contacts of an e-mailing service, e-mails, payment information, etc.
An example of malware in the insurance industry:

In May 2021, the company AXA Partnersa subsidiary of the French insurance giant, has been hit by a ransomware which damaged IT operations. Indeed, the ransomware managed to intercept some sensitive data that can be medical or financial. And there is no lack of examples. Insurance organizations are particularly exposed, as they handle a lot of sensitive personal data.
The previous summer, it was MMA that had to hastily bring its employees back on site while they were telecommuting, in order to counter a ransomware that had affected the insurer's business applications.
Don't forget! An effective cybersecurity organization is one with a CISO.
Phishing
Phishing is a cyberattack that consists in recovering the personal information of an Internet user or an organization. Phishing is particularly used to intercept victims' bank details. This method can be damaging for an individual as well as for a company employee.
Phishing is most of the time materialized by a fraudulent e-mail that impersonates an existing entity. It should be noted that companies in the banking and insurance sector are particularly affected by these cyber attacks.
The main types of phishing
Traditional phishing
Traditional phishing consists of impersonating a person to obtain confidential information and personal data. This widespread method is generally formalized by the usurpation of an individual's identity via his e-mail address. A traditional phishing campaign is often massive and untargeted.
Spear phishing
Spear phishing, unlike traditional phishing, targets a specific user or several employees of the same company. Here, cybercriminals gather as much information as possible about their victims and the people they are impersonating in order to make their target(s) fall into the trap.
Spear phishing allows the implementation of an equally popular method called the president scam (or BEC for Business Email Compromise). This is when a cybercriminal pretends to be the president of a company or group in order to build trust with the employees of the organization. The end goal is often to convince them to make an unscheduled international transfer to the cybercriminal organization.
The SMiShing
SMiShing, or SMS phishing, is the equivalent of traditional SMS phishing. These frauds are very common and much easier to set up because the layout requirements and customization possibilities are less, which makes it easier to spoof.
Misleading referencing
The DDos Attack
The DDos attack, or denial of serviceA DDoS attack is an attack whose sole purpose is to disable the operation of a service, a network, or a Web site. The DDoS attack consists of flooding the target server with connection requests or incoming messages in order to create a denial of service. To do this, cybercriminals hijack a very large number of computer systems and launch a targeted and grouped attack at a given moment. According to the latest WISR study, in 2019 there will be more than 8.4 million DDoS attacks.
Cybersecurity also means monitoring the vulnerability of applications. Are you interested? We also explain how to secure your application data.
The main DDoS attack vectors
Botnets
As seen above, DDoS attacks can be launched via botnets (networks of machines), in order to benefit from the simultaneous effect.
Reflection attacks
Amplification attacks
The amplification attack is a volumetric attack whose goal is to flood the bandwidth of the target network. This type of attack is made possible by modifying certain protocols to maximize the traffic generated on the network. This attack also has the particularity of generating a very large number of packets per second, which saturates the processing capacity of the target.
Cybercrime takes many forms, and attacks are becoming more and more frequent, regardless of sector or company size. It is therefore essential to call on specialists in the field of cybersecurity to define an effective defense strategy and set up reliable, watertight systems. For all these reasons, cybersecurity needs to be at the heart of a global strategy (see our article dedicated to the need to put cybersecurity at the heart of your Risk Management). It is therefore essential to implement Risk Management and internal control within the company.
From simple diagnostics to the most complex security projects, let our experts support you.




